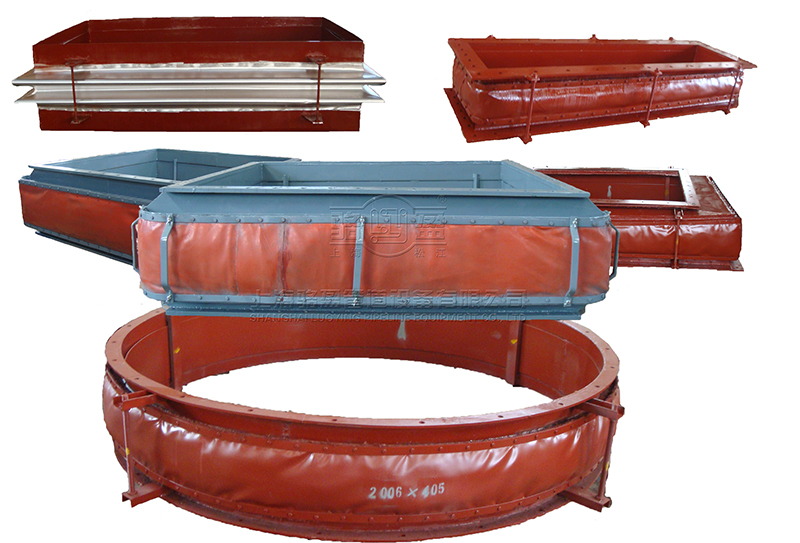
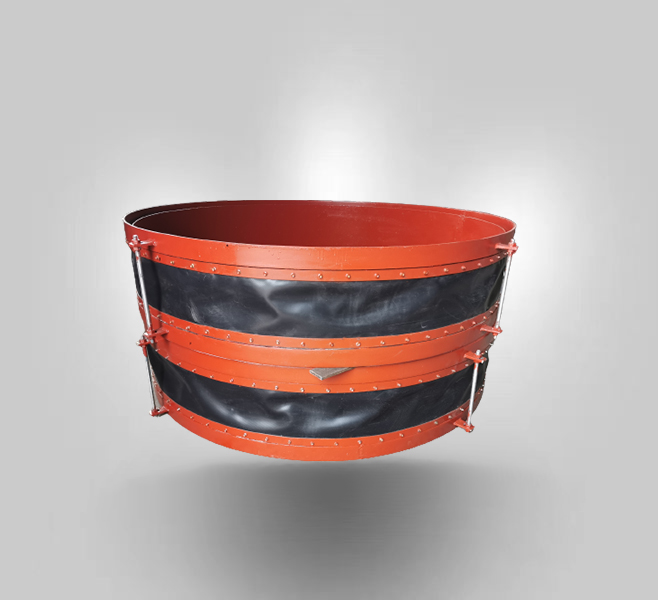
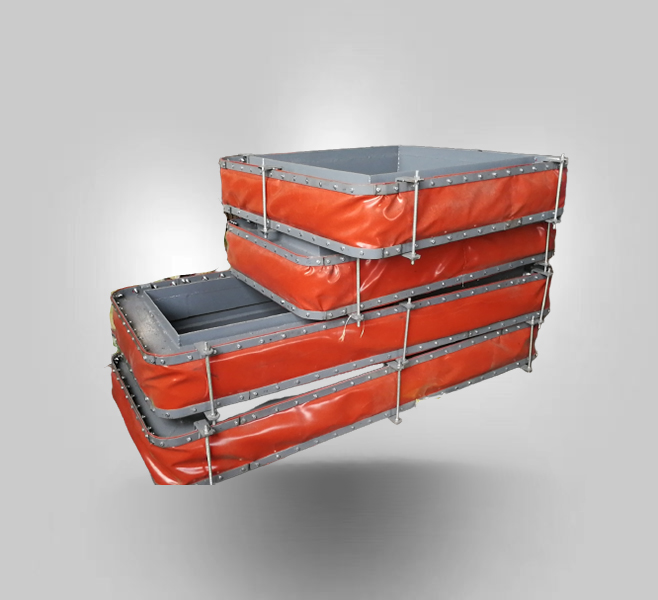
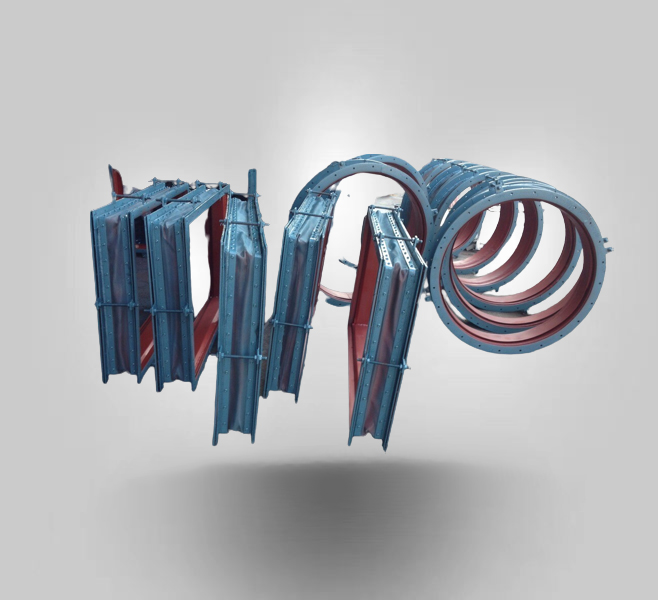
Fabric expansion joints
Fabric expansion joints perform a function of compensating for duct misalignment and duct thermal growth typically in power plants and other ducting systems. Fabric expansion joints are found wherever there is a need to convey hot media in low pressure applications such as “in flowing air” and “out flowing gas” in large combustion processes.
The fabric expansion joints provide both insulation and protection against wear, while effectively compensating for thermal growth and vibration.
The advantages and benefits of fabric expansion joints vary by the application, environment, and other factors related to an industrial process.
The fabric expansion joints offer superior flexibility and will handle large thermal movements, in a relatively short space.
Fabric expansion joints can absorb larger movements than metal expansion joints and do so without spring loads. This is critical to limiting thermally induced stresses in ducting, ducting supports, and related equipment.
These expansion joints are used to add flexibility to industrial ducting systems and fan/blower connections to absorb thermal growth, isolate vibration and noise, and allow for misalignments. Their large movements in a given space, small spring rates, and large temperature range give them advantage not available with other types of joints. They are needed in a wide array of industries, including power, petrochemical, pulp & paper, along with countless other industrial facilities. A variety of styles and materials are available to meet the specific requirements of any given application.
The high quality fully molded duct expansion joint types are made from reinforced rubber elastomers, and have the advantage of integral flanges and easy installation. They can be made with or without molded arches, which can provide additional movement and reliability.
Material:
Fluoroplastics (PTFE), Fluoroelastomer (FKM), neoprene (250F), and silicone (450F), If needed, the reinforcement can also be changed to aramid blend, polyester, and others.
Application:
Fossil Fired Power Plant, Pulp and Paper Plant, Air Heater to Coal Pulverizers, Cement, Clinker Cooler to Heat Exchanger, etc.
Media:
Oil, Clean air media, 600°F to 750°operating temperature, fuel gas media with heavy particulate
-
 Brand
BrandLUOYING
-
 Size
SizeDN5-300
-
 Temp
TempUp to 750 °C
-
 Pressure
PressureUp to 1 bar
Product Range
-

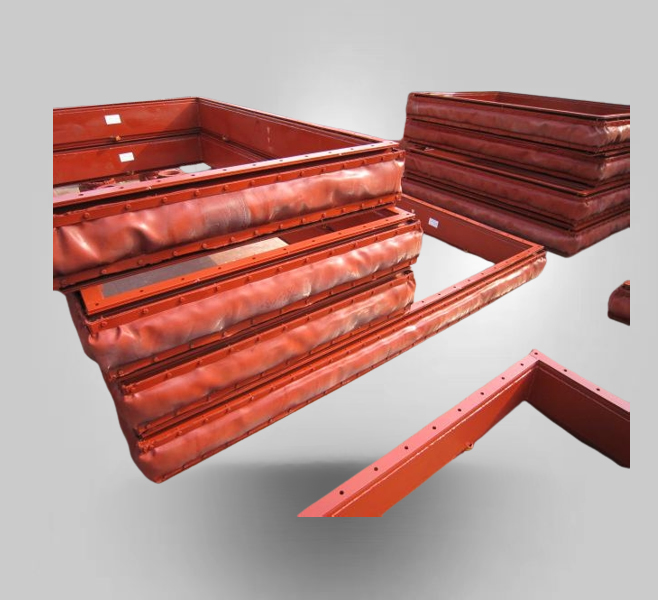
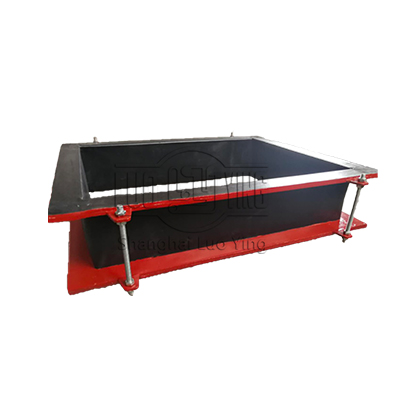
XB Rectangular Duct Fabric Expansion Joint
Rectangular duct fabric compensator is composed by rubber and fabric composite materials, steel flange, sleeve, thermal insulation materials. Mainly used in various fan, air duct for flexible connection. The function is shock absorption, noise reduction,
View More
-

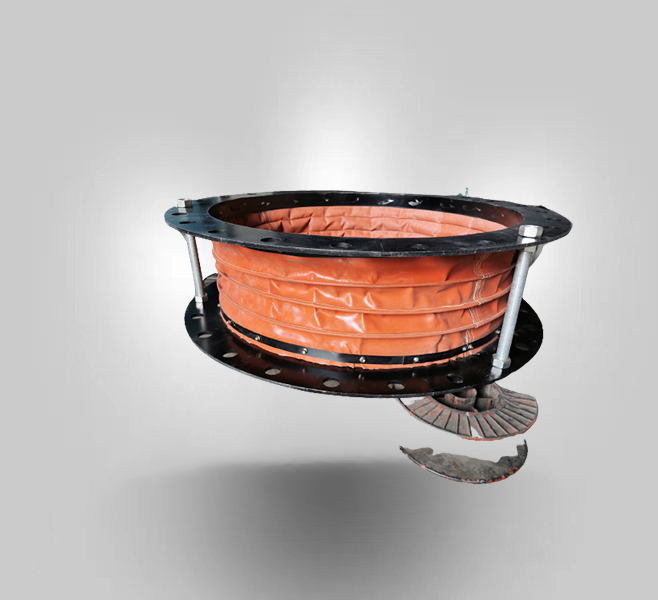
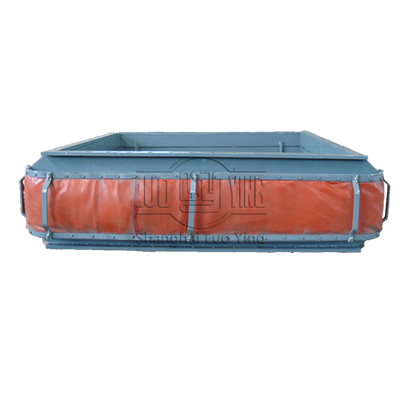
FVB Rectangular Air Flue Non-metal Expansion Joint
Air flue rubber joint compensator is composed by rubber composite materials, steel flange, sleeve, thermal insulation materials. Mainly used in various fan, air duct for flexible connection. The function is shock absorption, noise reduction, sealing, medi
View More
-
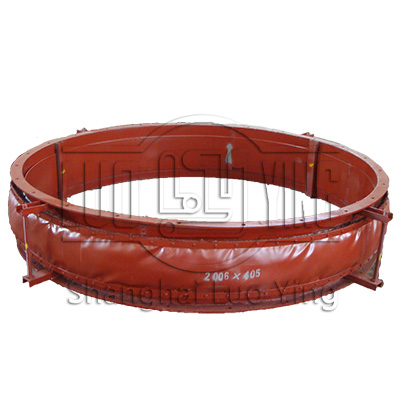

Duct Fabric Expansion Joint
LUOYING Fabric Expansion Joints are non-metallic flue duct expansion joints that provide stress relief for piping and ducting systems by absorbing thermal growth and shock, isolating mechanical vibration, and allowing for misalignments.LUOYING expansi
View More
-
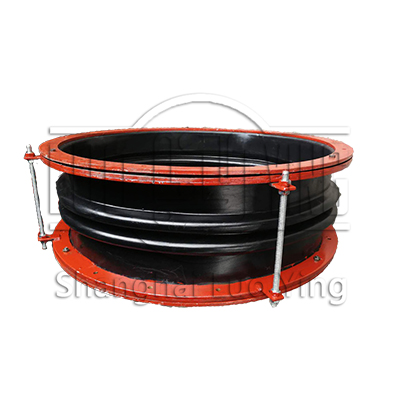

FUB Rubber Flue Duct Expansion Joint
Flue duct expansion jointsare custom engineered to handle low pressure (±3 psig) applications with temperatures ranging from -100°F to more than 2000°F. Industry Proven materials and precise engineering go into every LUOYING Fabric Expansion joint.
View More
Customized Products
Technical Notes
Fabric expansion joints and factors influencing their designFabric expansion joints and factors influencing their design
The fabric belt joint types combine different steel frame types and industry proven materials and options. In some instances, additional components such as insulation pillows, accumulation barriers or flow liners are used to help protect the fabric material. The basics are shown below, but a number of other design elements are possible.
The guiding principle for fabric joint design is to protect the fabric belt element so that it can absorb movement while retaining the media.
The longevity of the belt life can be diminished by many factors. These factors include excessive temperature, harsh corrosives, exposure to abrasive particulate, excessive movements, fly ash weight against the belt, and high internal pressures. All of these problems can be solved if they are anticipated. The quality of the expansion joint design is only as good as the information provided up front. A realistic and accurate analysis of the system is step one. Assuming that is taken care of, these guidelines are a brief introduction to factors that influences the success of the expansion joint.
How Does a Fabric Expansion Joint Work?
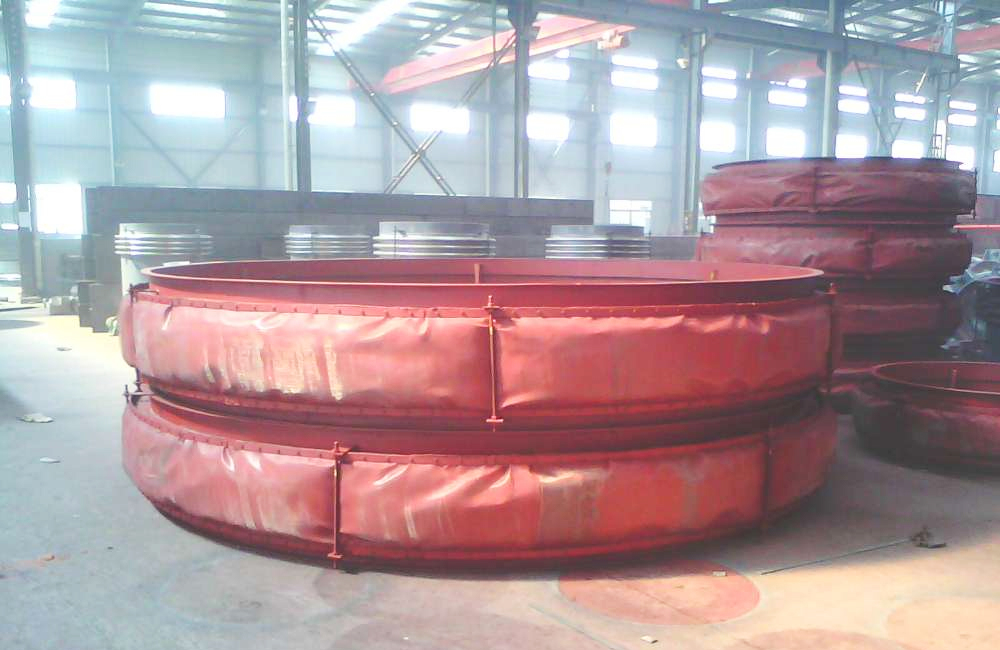

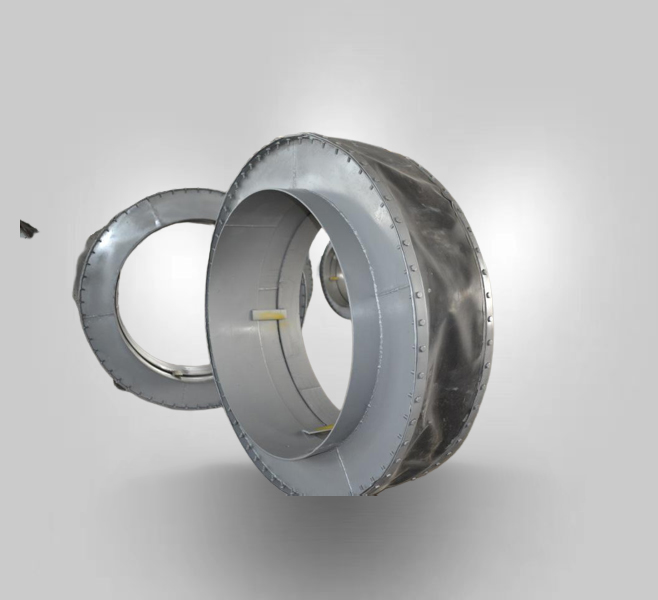
A fabric expansion joint is inserted into a gap in the duct work where movement will occur. A fabric expansion joint has two main components — the fabric gas seal and the metal frames. The fabric gas seal is a closed loop, like a belt, with its two edges clamped all around to the metal frames that are in turn connected to the end of ducting. The belt type uses a flat belt flexible element made as a flat belt, and is versatile and effective in terms of manufacture and installation. And they allow many different types of frames to suit operating conditions.
As the ducting moves, the fabric belt deforms. The fabric material must do this without tearing or leaking while sometimes being exposed to high temperatures and/or corrosive media.
Advantage
Nsure that the hose meets the published levels.-
flexibility
Excellent movement absorption and flexibility. -
reduction
Noise reduction. -
costs
Significant costs savings of both manufacturing and installation labor. -
Elimination
Elimination of the risk of installing sensitive assemblies at the job site. -
materials
Good vibration resistance depending on design and materials. -
customized
we could also make design according to your working requirements, or we make production according to your drawing.
Expansion joint accessories
Quality decides value-

Flange
Piping components can be bolted together between flanges. Flanges are used to connect pipes with each other, to valves, to fittings, and to specialty items such as strainers and pressure vessels. A cover plate can be connected to create a "blind flange" Flanges are joined by bolting, and sealing is often completed with the use of gaskets or other methods. Mechanical means to mitigate effects of leaks, like spray guards or specific spray flanges, may be included. Industries where flammable, volatile, toxic or corrosive substances are being processed have greater need of special protection at flanged connections. Flange guards can provide that added level of protection to ensure safety.
-

Covers
Fasteners are used for fastening and securing materials such as wood, metal, plastic, or concrete. They include nuts and bolts, threaded rods, structural bolts, machine screws, wedge anchors, washers, rivets, and more in a variety of types and sizes, including metric and inch.
-

Particulate barriers/purge connectors
In systems that have a media with significant particulate content (i.e. flash or catalyst), a barrier of ceramic fiber can be utilized to prevent corrosion and restricted bellows flexibility resulting from the accumulation of the particulate. Purge connectors may also be utilized to perform this same function. Internal liners must also be included in the design if the expansion joint includes purge connectors or particulate barriers.
-
Liners
A gasket is a mechanical seal which fills the space between two or more mating surfaces, generally to prevent leakage from or into the joined objects while under compression. It is a deformable material that is used to create a static seal and maintain that seal under various operating conditions in a mechanical assembly.